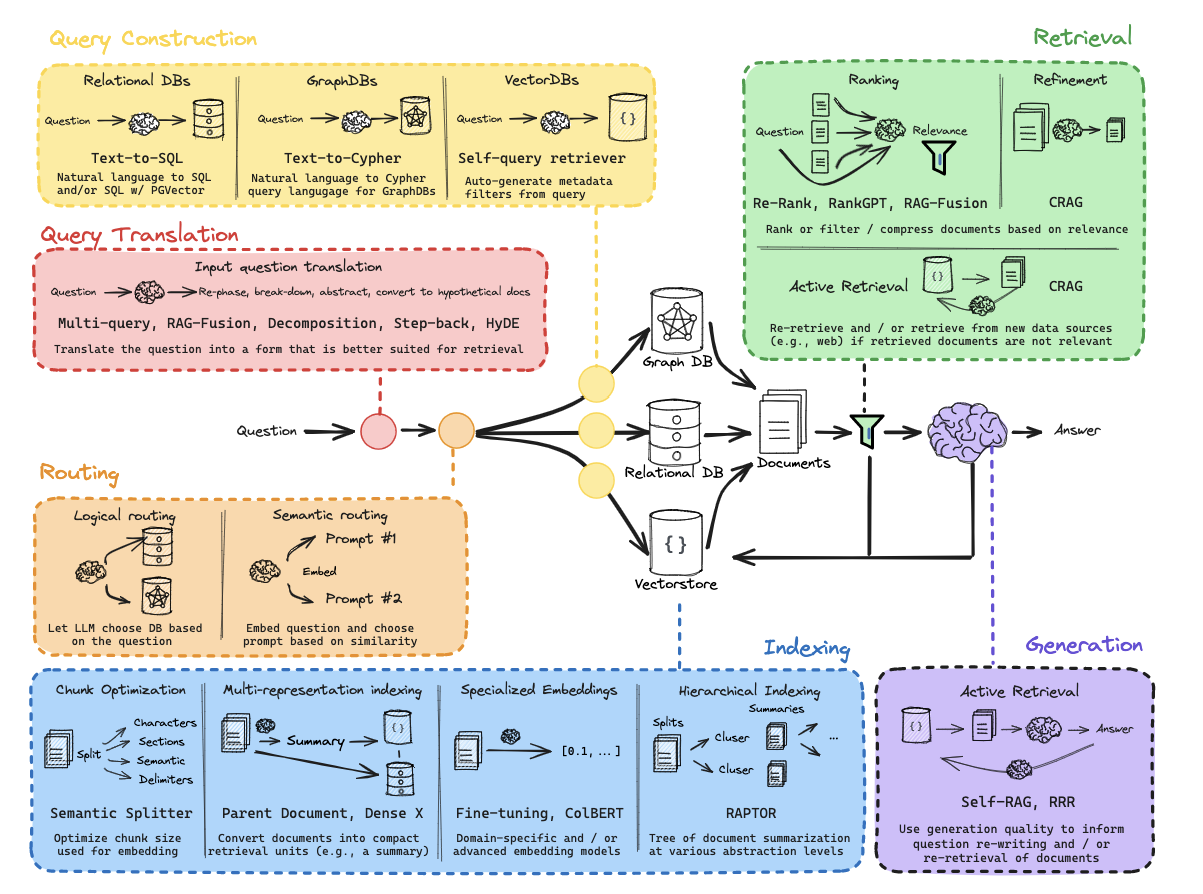
从零开始的RAG:路由
环境
(1) 包
1 ! pip install langchain_community tiktoken langchain-openai langchainhub chromadb langchain youtube-transcript-api pytube
(2) LangSmith
https://docs.smith.langchain.com/
1 2 3 4 import osos.environ['LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2' ] = 'true' os.environ['LANGCHAIN_ENDPOINT' ] = 'https://api.smith.langchain.com' os.environ['LANGCHAIN_API_KEY' ] = <your-api-key>
(3) API 密钥
1 os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY' ] = <your-api-key>
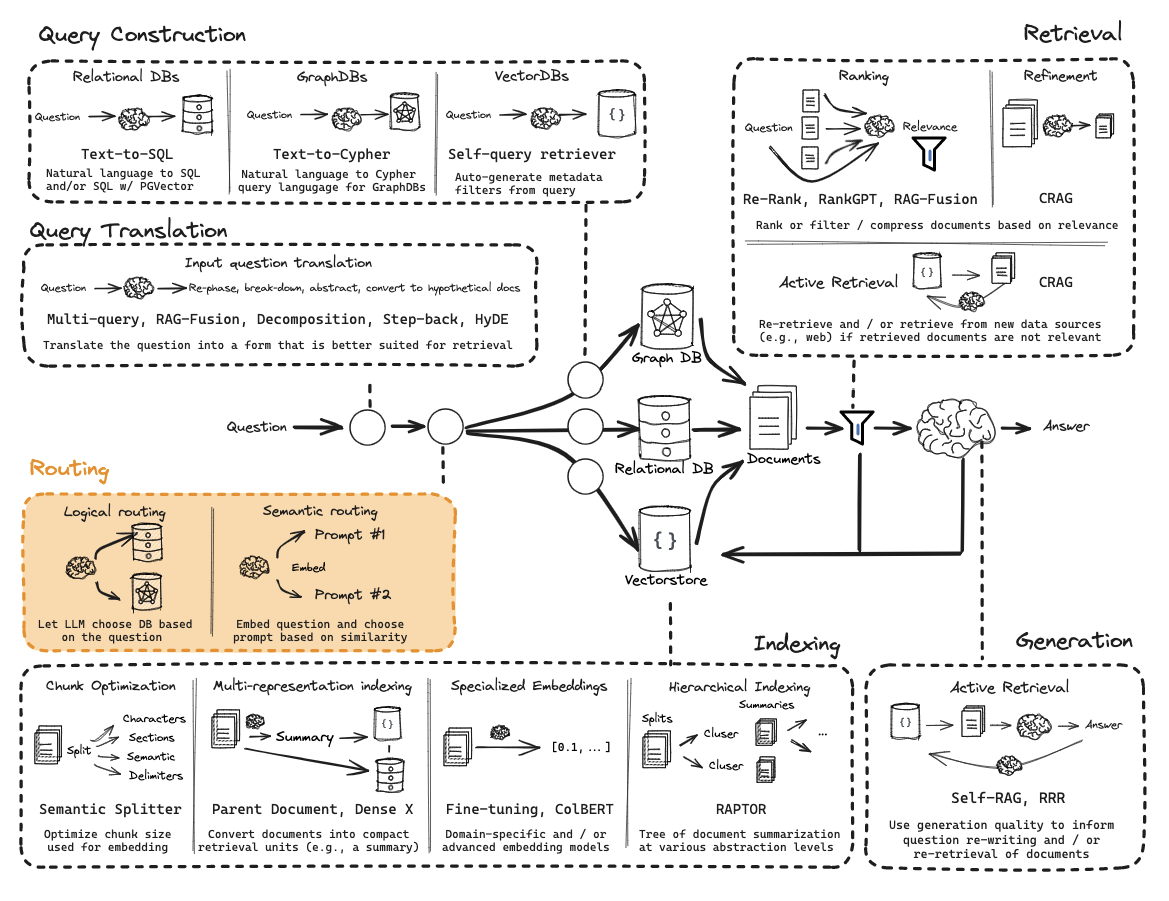
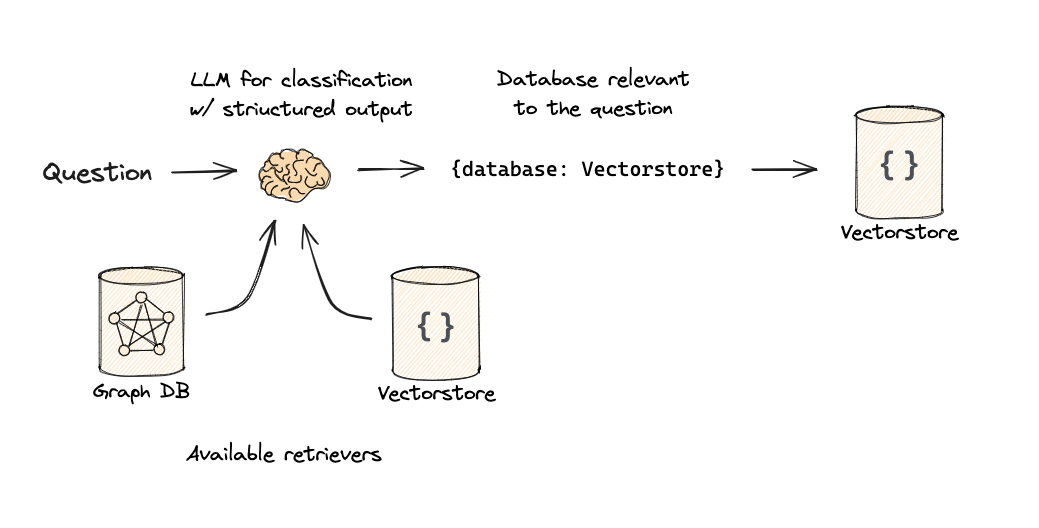
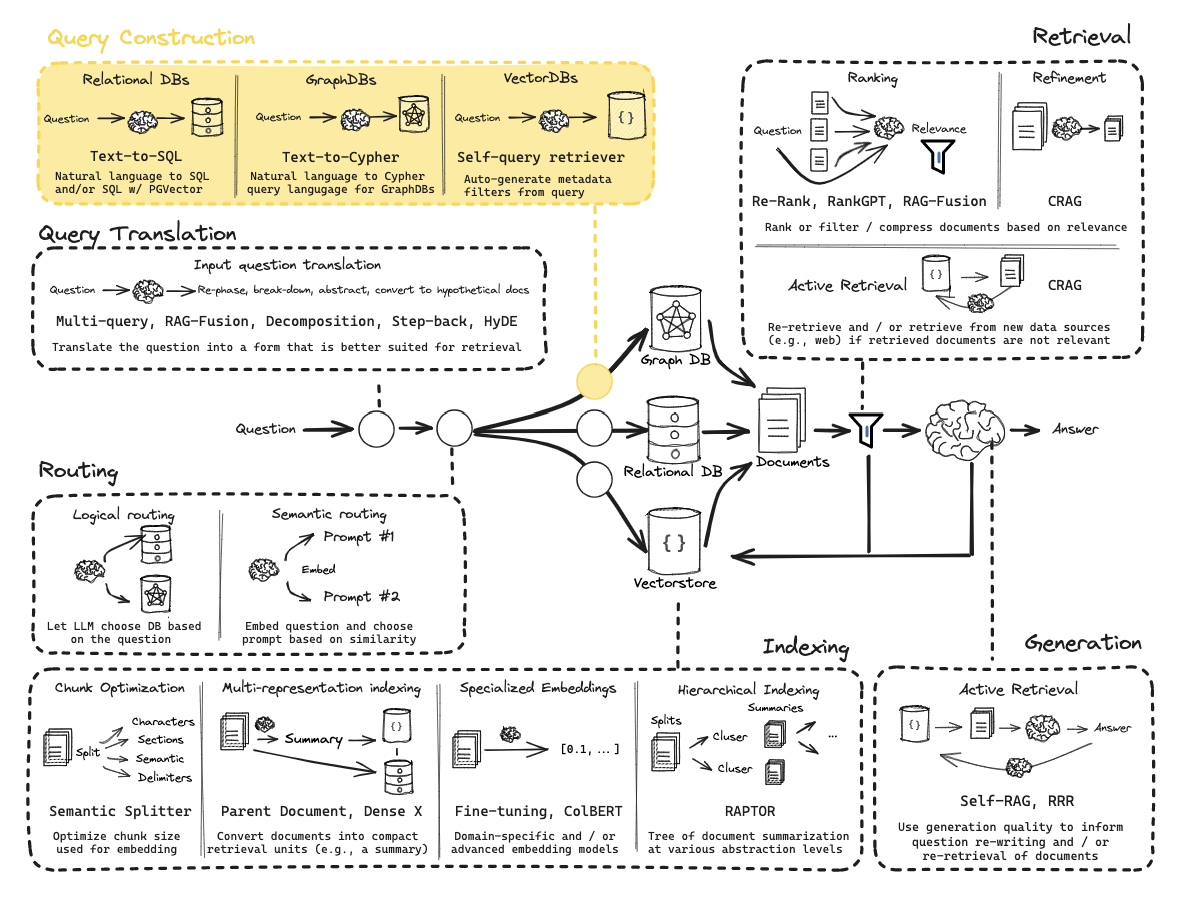
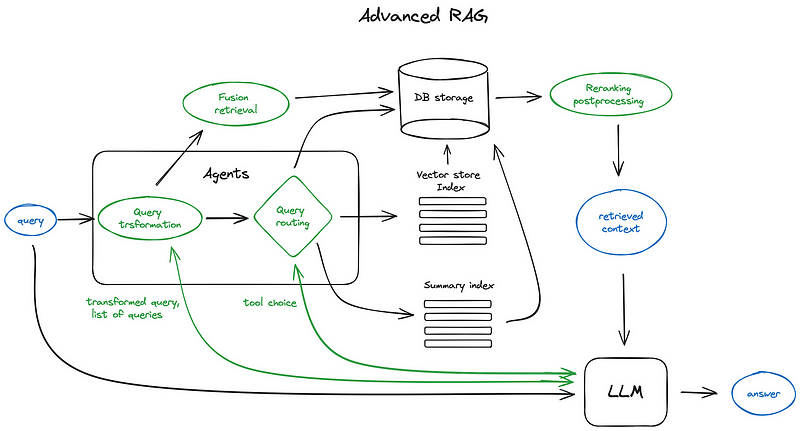
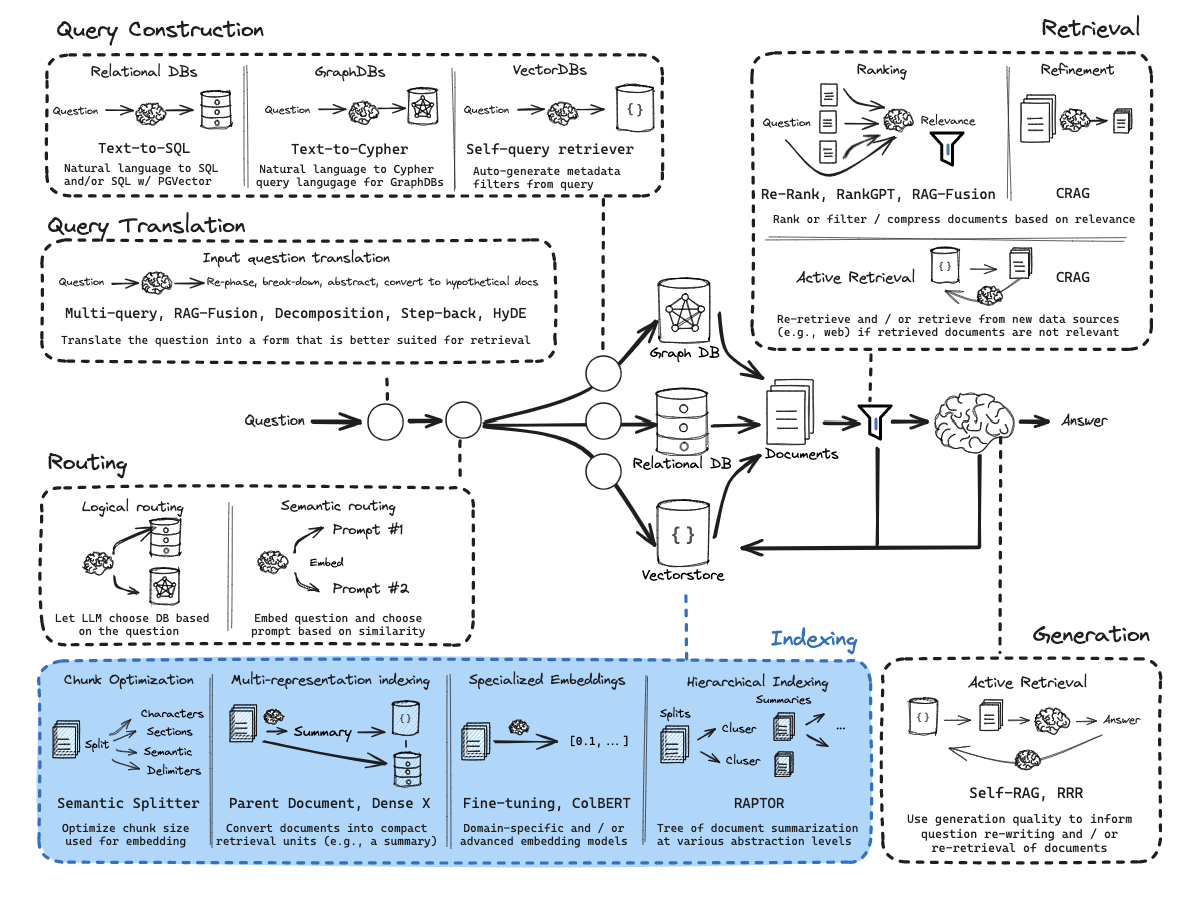
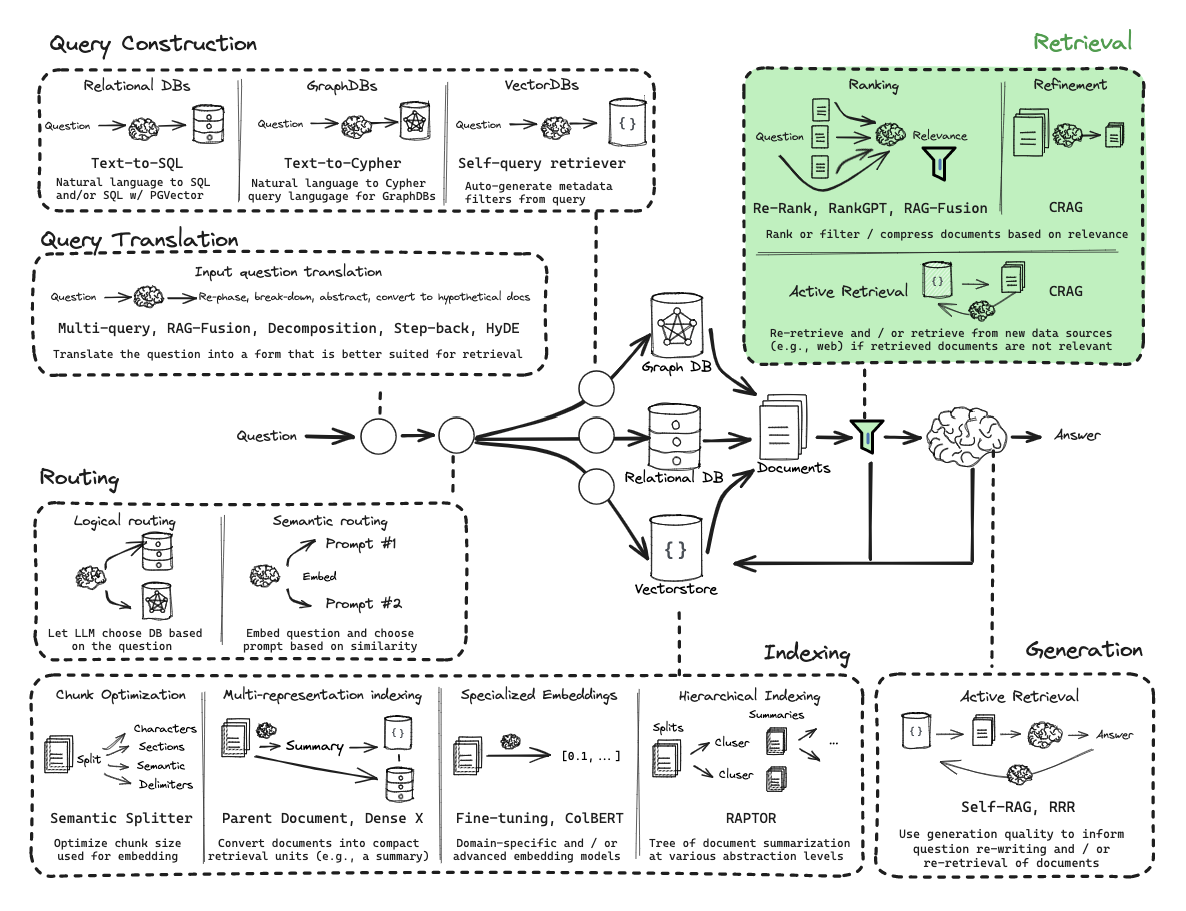
第10部分:逻辑和语义路由
使用函数调用进行分类。
流程:
文档:
https://python.langchain.com/docs/use_cases/query_analysis/techniques/routing#routing-to-multiple-indexes
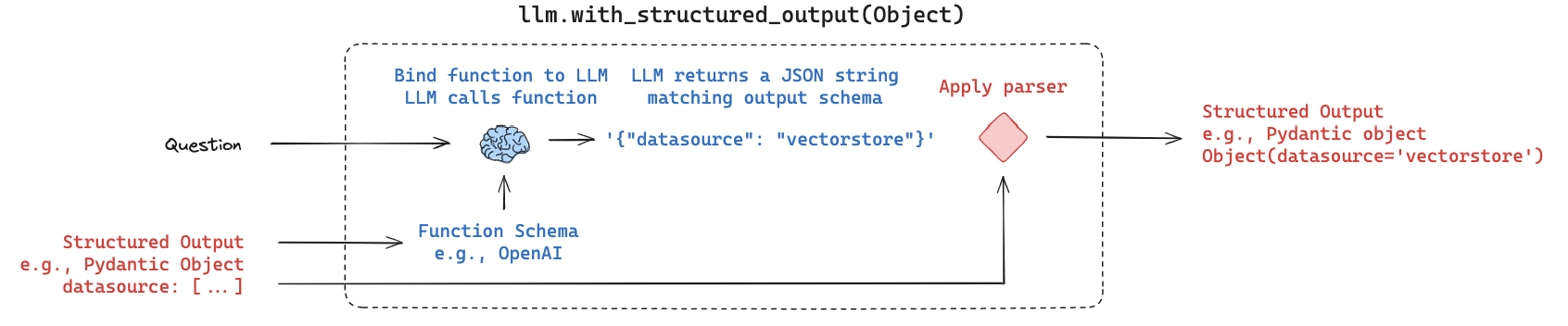
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 from typing import Literal from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatefrom langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Fieldfrom langchain_openai import ChatOpenAIclass RouteQuery (BaseModel ): """将用户查询路由到最相关的数据源。""" datasource: Literal ["python_docs" , "js_docs" , "golang_docs" ] = Field( ..., description="根据用户问题选择哪个数据源最适合回答他们的问题" , ) llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125" , temperature=0 ) structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(RouteQuery) system = """你是将用户查询路由到适当数据源的专家。 根据问题所指的编程语言,将其路由到相关数据源。""" prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages( [ ("system" , system), ("human" , "{question}" ), ] ) router = prompt | structured_llm
注意:我们使用函数调用来生成结构化输出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 question = """Why doesn't the following code work: from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(["human", "speak in {language}"]) prompt.invoke("french") """ result = router.invoke({"question" : question})
一旦我们有了这个,就很容易定义一个使用result.datasource的分支
https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/how_to/routing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 def choose_route (result ): if "python_docs" in result.datasource.lower(): return "chain for python_docs" elif "js_docs" in result.datasource.lower(): return "chain for js_docs" else : return "golang_docs" from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambdafull_chain = router | RunnableLambda(choose_route)
1 full_chain.invoke({"question" : question})
追踪:
https://smith.langchain.com/public/c2ca61b4-3810-45d0-a156-3d6a73e9ee2a/r
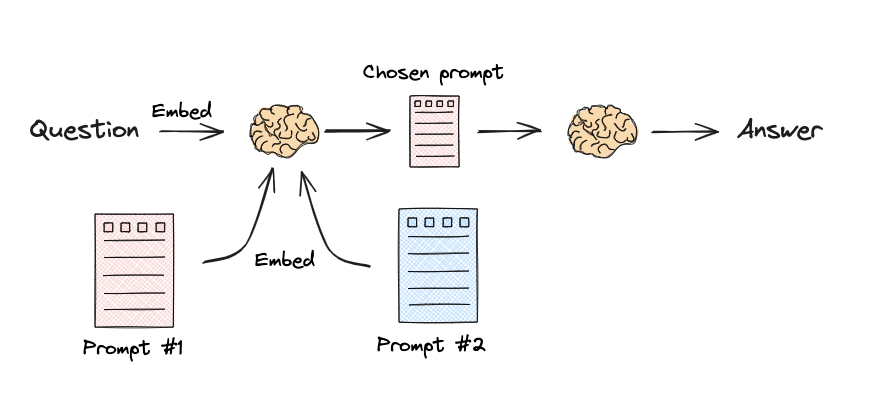
语义路由
流程:
文档:
https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/cookbook/embedding_router
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 from langchain.utils.math import cosine_similarityfrom langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParserfrom langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplatefrom langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda, RunnablePassthroughfrom langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddingsphysics_template = """你是一位非常聪明的物理学教授。\ 你擅长以简洁易懂的方式回答物理问题。\ 当你不知道问题的答案时,你承认你不知道。 这是一个问题: {query}""" math_template = """你是一位非常优秀的数学家。你擅长回答数学问题。\ 你之所以如此优秀,是因为你能够将难题分解为其组成部分,\ 回答组成部分,然后将它们组合起来回答更广泛的问题。 这是一个问题: {query}""" embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings() prompt_templates = [physics_template, math_template] prompt_embeddings = embeddings.embed_documents(prompt_templates) def prompt_router (input query_embedding = embeddings.embed_query(input ["query" ]) similarity = cosine_similarity([query_embedding], prompt_embeddings)[0 ] most_similar = prompt_templates[similarity.argmax()] print ("Using MATH" if most_similar == math_template else "Using PHYSICS" ) return PromptTemplate.from_template(most_similar) chain = ( {"query" : RunnablePassthrough()} | RunnableLambda(prompt_router) | ChatOpenAI() | StrOutputParser() ) print (chain.invoke("What's a black hole" ))
追踪:
https://smith.langchain.com/public/98c25405-2631-4de8-b12a-1891aded3359/r
从零开始的RAG:查询构建
有关图和SQL,请参阅有用资源:
https://blog.langchain.dev/query-construction/
https://blog.langchain.dev/enhancing-rag-based-applications-accuracy-by-constructing-and-leveraging-knowledge-graphs/
第11部分:元数据过滤的查询结构化
流程:
许多向量存储包含元数据字段。
这使得可以根据元数据过滤特定的块。
让我们看看在YouTube转录数据库中可能看到的一些示例元数据。
文档:
https://python.langchain.com/docs/use_cases/query_analysis/techniques/structuring
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from langchain_community.document_loaders import YoutubeLoaderdocs = YoutubeLoader.from_youtube_url( "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pbAd8O1Lvm4" , add_video_info=True ).load() docs[0 ].metadata
假设我们已经构建了一个索引:
允许我们对每个文档的contents和title进行非结构化搜索
并对view count、publication date和length进行范围过滤。
我们希望将自然语言转换为结构化搜索查询。
我们可以为结构化搜索查询定义一个模式。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import datetimefrom typing import Literal , Optional , Tuple from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Fieldclass TutorialSearch (BaseModel ): """在关于软件库的教程视频数据库中搜索。""" content_search: str = Field( ..., description="应用于视频转录的相似性搜索查询。" , ) title_search: str = Field( ..., description=( "应用于视频标题的内容搜索查询的替代版本。" "应该简洁,只包含可能在视频标题中的关键词。" ), ) min_view_count: Optional [int ] = Field( None , description="最小观看次数过滤器,包含。仅在明确指定时使用。" , ) max_view_count: Optional [int ] = Field( None , description="最大观看次数过滤器,不包含。仅在明确指定时使用。" , ) earliest_publish_date: Optional [datetime.date] = Field( None , description="最早的发布日期过滤器,包含。仅在明确指定时使用。" , ) latest_publish_date: Optional [datetime.date] = Field( None , description="最新的发布日期过滤器,不包含。仅在明确指定时使用。" , ) min_length_sec: Optional [int ] = Field( None , description="最小视频长度(秒),包含。仅在明确指定时使用。" , ) max_length_sec: Optional [int ] = Field( None , description="最大视频长度(秒),不包含。仅在明确指定时使用。" , ) def pretty_print (self ) -> None : for field in self.__fields__: if getattr (self, field) is not None and getattr (self, field) != getattr ( self.__fields__[field], "default" , None ): print (f"{field} : {getattr (self, field)} " )
现在,我们提示LLM生成查询。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatefrom langchain_openai import ChatOpenAIsystem = """你是将用户问题转换为数据库查询的专家。\ 你可以访问一个关于构建LLM应用程序的软件库的教程视频数据库。\ 给定一个问题,返回一个优化的数据库查询以检索最相关的结果。 如果有你不熟悉的缩写或单词,不要尝试重新措辞它们。""" prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages( [ ("system" , system), ("human" , "{question}" ), ] ) llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125" , temperature=0 ) structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(TutorialSearch) query_analyzer = prompt | structured_llm
1 query_analyzer.invoke({"question" : "rag from scratch" }).pretty_print()
1 2 3 query_analyzer.invoke( {"question" : "videos on chat langchain published in 2023" } ).pretty_print()
1 2 3 query_analyzer.invoke( {"question" : "videos that are focused on the topic of chat langchain that are published before 2024" } ).pretty_print()
1 2 3 4 5 query_analyzer.invoke( { "question" : "how to use multi-modal models in an agent, only videos under 5 minutes" } ).pretty_print()
要将其连接到各种向量存储,您可以在这里 查看。